5.5 KiB
ltchiptool
ltchiptool is a universal, easy-to-use GUI flashing/dumping tool for BK7231, RTL8710B and RTL8720C. It also contains some CLI utilities for binary firmware manipulation.
Installation
GUI package (Windows only)
Download the latest release .EXE from the GitHub Releases page. Open the file, and you're ready to go!
The GUI executable works on Windows 7 and newer.
GUI or CLI (Windows/Linux/etc.)
Install the package from PyPI, using pip install ltchiptool.
This will install ltchiptool and uf2tool packages. You can start the GUI by typing python -m ltchiptool gui.
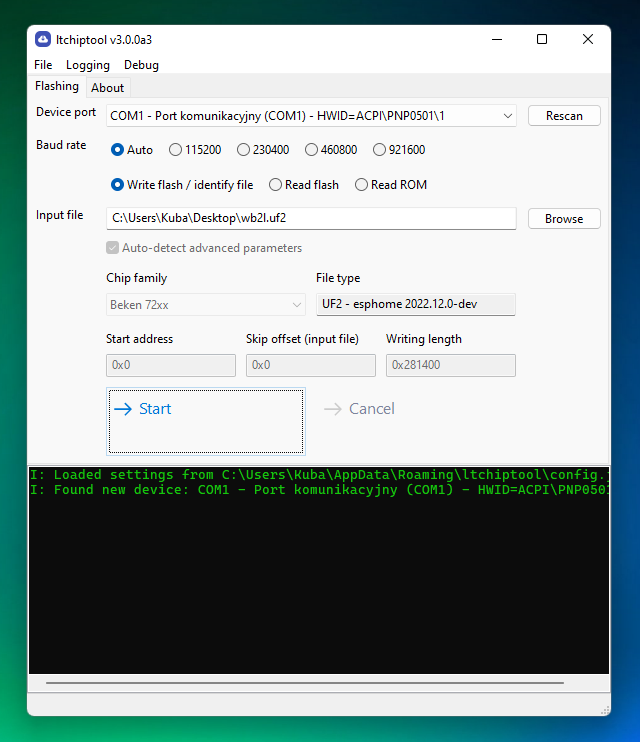
GUI Usage
The main window is somewhat similar to NodeMCU PyFlasher.
- For dumping, choose
Read flash. If you've previously chosen an input or output file, it will generate a dump filename with the current timestamp and chip type. Otherwise, clickBrowseand choose the output file. By default, the tool will attempt to read the entire flash chip (usually 2 MiB). - For flashing, choose
Write flash. ClickBrowseand select any valid firmware file. The file type and chip type will be auto-detected, along with correct flash offset and length. No need to worry about overwriting the bootloader anymore!- If the file you're selecting is
UnrecognizedorNot flashable, it's most likely not a valid firmware file. Refer to usage guides of the custom firmware project of choice, to find which file is meant for flashing.
- If the file you're selecting is
- It's best to leave
Auto-detect advanced parameterschecked. If you're an experienced user and want to flash custom areas of the flash, uncheck the box and specify the parameters manually. - When you're ready, hit
Start. The tool will try to connect to the chip on the selected UART port. The black log window will print any warnings/errors, as well as a short guide on how to put the chip in download mode.
!!! info
LibreTuya generates multiple firmware files in the build directory. You usually want to flash the .uf2 file, but since ltchiptool can detect file types, you can choose a different firmware file and it'll tell you if that works.
CLI Usage
!!! note If you're here to learn how to flash or dump firmware files, use the instructions above.
The content below serves as a short documentation page for [`ltchiptool`](https://github.com/libretuya/ltchiptool) and is mostly meant for advanced users.
$ ltchiptool --help
Usage: ltchiptool [OPTIONS] COMMAND [ARGS]...
Tools for working with LT-supported IoT chips
Options:
-v, --verbose Output debugging messages (repeat to output more)
-T, --traceback Print complete exception traceback
-t, --timed Prepend log lines with timing info
-r, --raw-log Output logging messages with no additional styling
-i, --indent INTEGER Indent log messages using graph lines
-V, --version Show the version and exit.
-h, --help Show this message and exit.
Commands:
dump Capture or process device dumps
elf2bin Generate firmware binaries from ELF file
flash Flashing tool - reading/writing
link2bin Link code to binary format
list List boards, families, etc.
soc Run SoC-specific tools
uf2 Work with UF2 files
Flashing/dumping
There are three main commands used for flashing:
ltchiptool flash file <FILE>- detect file type based on its contents (i.e. chip from which a dump was acquired), similar to Linuxfilecommandltchiptool flash read <FAMILY> <FILE>- make a full flash dump of the connected device; specifying the family is requiredltchiptool flash write <FILE>- upload a file to the device; detects file type automatically (just like thefilecommand above)
Supported device families can be checked using ltchiptool list families command. In the commands above, you can use any of the family names (name/code/short name/etc).
The upload UART port and baud rate is detected automatically. To override it, use -d COMx or -d /dev/ttyUSBx. To change the target baud rate, use -b 460800.
Note that the baud rate is changed after linking. Linking is performed using chip-default baud rate.
It's not required to specify chip family for writing files - ltchiptool tries to recognize contents of the file, and chooses the best settings automatically.
If you want to flash unrecognized/raw binaries (or fine-tune the flashing parameters), specify -f <FAMILY> and -s <START OFFSET>.
UF2 Example
$ ltchiptool uf2 info ./arduinotest_22.08.01_wb2l_BK7231T_lt0.8.0.uf2
Family: BK7231T / Beken 7231T
Tags:
- BOARD: wb2l
- DEVICE_ID: d80e20c2
- LT_VERSION: 0.8.0
- FIRMWARE: arduinotest
- VERSION: 22.08.01
- OTA_VERSION: 01
- DEVICE: LibreTuya
- BUILD_DATE: 6d08e862
- LT_HAS_OTA1: 01
- LT_HAS_OTA2: 00
- LT_PART_1: app
- LT_PART_2:
Data chunks: 1871
Total binary size: 478788